Inflation and Gold’s Relationship
Inflation is often seen as a key driver of gold prices because investors look to protect their wealth when economic strains threaten the dollar's value.
Gold's value has a complex relationship with inflation. It is influenced by various economic factors determining whether it acts as a reliable hedge. Understanding this connection is essential for anyone considering gold as a long-term investment or inflation hedge.
Gold Rush, a Denver gold buyer, is here to help people maximize the value of their precious metals and diamonds. Our experts will guide you through the process of assessing value and market price for your items. Come on by if you need to sell gold, silver, platinum, palladium, or diamonds!
Key Takeaways
-
Gold as a hedge: Gold is frequently viewed as a safeguard against rising inflation.
-
Influence of interest rates: Rising rates can impact gold’s appeal as an investment.
-
Broader economic factors: Gold prices respond to more than just inflation.
-
Historical patterns: Gold’s inflation response has varied over the decades.
-
Investment insights: Knowing when inflation affects gold can aid in smart investing.
The Relationship Between Inflation and Gold Prices
The link between inflation and gold prices is often complex.
Generally, high inflation drives investors toward gold because it’s perceived as a stable store of value.
When a currency's purchasing power declines, investors look for assets that preserve wealth (gold). Its tangible value is attractive in times when inflation erodes the dollar’s buying power. This increase in demand drives up the value of gold.
However, this relationship isn’t always straightforward.
Historical data shows periods when inflation and gold prices align and other times when they don’t. For example, in the 1980s, high inflation led to a gold price surge, but in recent decades inflation and gold have not always moved in sync.
Various factors, such as economic stability, the strength of the U.S. dollar, and global demand for commodities, add complexity to this relationship.
How Interest Rates Affect Gold Prices During Inflation
When inflation rises, central banks often respond by raising interest rates. This can have a significant impact on gold prices.
Higher interest rates make other investments, like bonds, more appealing since they offer steady returns. As a result, gold, which doesn’t yield interest, may lose some of its appeal during periods of high rates.
Key Impacts of Interest Rates on Gold
-
High rates reduce gold’s appeal by increasing bond yields.
-
Low rates often support gold prices by lowering opportunity costs.
-
Interest-bearing alternatives can attract investors away from gold.
-
Rising rates can signal a cooling economy, impacting demand.
-
Low inflation with high rates may create unique investment conditions.
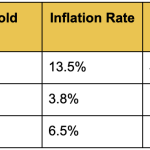
Historical Data: Gold Prices During Inflationary Periods
Gold's response to inflation has varied significantly over time.
During some inflationary periods, gold prices surged. At other times they remained steady or even fell.
For instance, in the 1980s, stagflation drove gold prices higher, while the 2008 financial crisis saw gold become a safe-haven asset as inflation began to rise post-crisis.
Gold Prices During Key Inflationary Periods
Inflation's Influence on Gold as a Long-Term Investment
Inflation often influences gold’s appeal over the long term, but it’s just one piece of a larger puzzle.
Investors have traditionally turned to gold during inflationary times because it’s seen as a “no-default” asset - meaning its value isn’t tied to any entity that could go bankrupt or default.
This stability makes gold attractive for those looking to preserve wealth through economic ups and downs. The more inflation rises, the more people view gold as a safe bet, especially in comparison to currencies that may lose purchasing power.
Gold’s liquidity is another factor that enhances its appeal. It’s easy to buy and sell. Investors can quickly access their capital if needed.
Over the decades, gold has developed a reputation as a reliable store of value, which continues to make it a compelling option for those seeking a stable investment that stands the test of time.
Factors Beyond Inflation That Drive Gold Prices
Dollar Strength and Gold
Gold prices are closely tied to the strength of the U.S. dollar.
When the dollar weakens, gold prices tend to rise because gold becomes cheaper for foreign buyers - increasing demand.
In contrast, a strong dollar often means lower gold prices, as it makes gold more expensive globally - leading to a decrease in purchasing interest.
Government Deficits and Market Confidence
Government spending and national debt levels can also impact gold prices.
Large deficits may weaken the dollar - which can make gold more attractive as an investment.
Investors often turn to gold when confidence in currency stability is low, viewing it as a reliable alternative in times of economic uncertainty.
Global Geopolitical Instability
Geopolitical events, from wars to political upheavals, often drive investors toward gold.
Times of global instability reveal gold’s status as a safe-haven. It’s not directly tied to any specific government or currency so it is more stable.
When traditional markets appear vulnerable, gold serves as a protective measure for those seeking to shield their investments from unpredictable events.
Frequently Asked Questions on Inflation and Gold Prices
Why Is Gold Considered a Hedge Against Inflation?
Gold is considered an inflation hedge because it tends to hold its value when currency values fall. When inflation rises, the purchasing power of cash decreases, making tangible assets like gold attractive for wealth preservation.
Will Gold Prices Drop If Inflation Declines?
Gold prices don’t necessarily fall when inflation eases. Other factors, like market sentiment, currency strength, and global economic conditions, often play a role in determining gold’s price direction, regardless of inflation trends.
How Can I Invest in Gold During Inflation?
There are multiple ways to invest in gold, such as buying physical gold, purchasing ETFs, or investing in mining stocks. Physical gold and ETFs are popular during inflationary periods for their accessibility, while mining stocks offer potential growth tied to gold’s market performance.
Conclusion: Gold and Inflation—What It Means for Investors
Gold’s relationship with inflation is intricate and influenced by a variety of economic factors. While inflation tends to drive interest in gold, elements like interest rates, the dollar's strength, and global stability also shape gold’s value in the market.
This is why we at Gold Rush take so much pride in serving our communities with expert, honest gold-buying services. Precious metals and diamonds transcend our currencies and policies. They hold real value determined by weight and purity and people need experts to help them maximize their profits when its time to sell.
Trust Gold Rush to deliver the most rewarding experience when it comes to selling your gold.